Tannins are naturally occurring organic compounds commonly found in tree bark, leaves, and fruits. In horticulture, tannins are found in growing medium will affect the growth of plants. This article will provide detailed but easy to understand information about tannins, their effects on growing media and how to deal with them effectively.
What is Tannin?
Tannin belongs to the polyphenol group, known as a substance that can combine with proteins and heavy metals. In nature, tannin has the effect of protecting plants from pathogenic microorganisms and predators. The main source of tannins in growing media usually comes from:
- Bark, trunk: Oak bark, pine bark.
- Leaf: Leaves such as coconut leaves, acacia leaves, oak leaves.
- Fruit: Coconut shell, grape skin, seeds
Tannins are divided into two main types based on chemical structure and decomposition characteristics
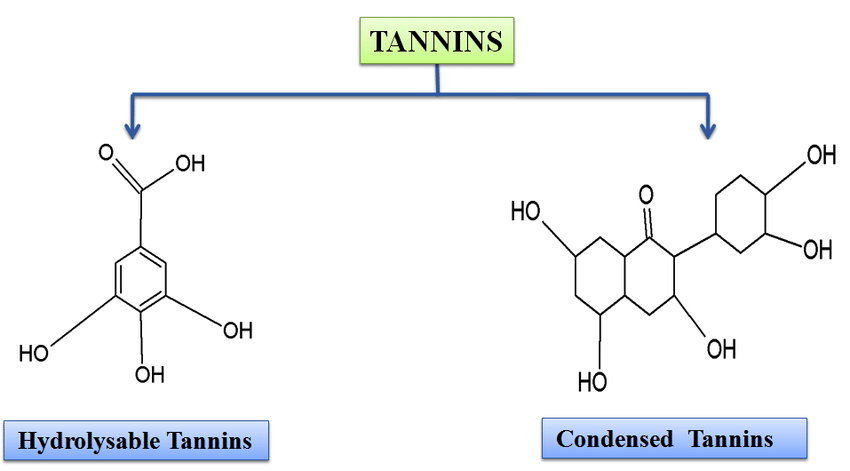
Condensed Tannins
Condensed tannins are formed from flavonoid units linked together. They are common in plants, especially wood, bark, and seeds.
Hydrolyzable Tannins
Hydrolyzable tannins consist of polyphenol compounds bound to sugars or phenolic acids (such as gallic acid or ellagic acid).
“Coconut shells are used as a growing medium but contain a lot of tannins”
5 effects of tannin in growing medium

1. Change the pH of the soil
Tannins are acidic and can lower the pH of the growing medium, which affects the plant's ability to absorb nutrients.
See also: Độ pH cho cây trong nhà: giải thích, hướng dẫn chi tiết
2. Effects on beneficial microorganisms
Tannins have antibacterial properties that can kill or inhibit the growth of beneficial microorganisms in the soil, such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria or mycorrhizae. This reduces the efficiency of nutrient absorption by the roots.
3. Potential toxicity to plants
If tannin concentrations are too high, they can be toxic to plant roots, slowing growth or causing root burn.
4. Reduced ability to absorb nutrients
Tannin combines with iron and precipitates minerals, making it impossible for plants to absorb them. important nutrients.
5. Impact on soil structure
As tannin accumulates in the soil, it can interact with other organic compounds, changing the soil structure. This can reduce drainage and aeration, negatively affecting root growth.
Signs of plants affected by tannins

- Yellow or withered leaves: Plants do not absorb enough nutrients, causing leaves to turn yellow or wither.
- Slow root growth: The root system is weakened, resulting in slow or no growth of the plant.
- Root burn phenomenon: White or brown root areas may be a sign of burning due to the action of tannins.
- Low microbial yield: Limit biological processes in the substrate, resulting in poor soil fertility.
How to handle tannin in growing medium

Method 1: Soak the fabric in water
Before using growing media such as coconut peat, coconut fiber, coconut lumps or bark, soak and wash with water to remove excess tannin. In coconut fiber, tannin content is about 2.5%, has a salty taste, is soluble in water but precipitates protein, so it is necessary to remove tannin in coconut fiber before planting.
Method 2: Soak with lime
Tannin is an acidic organic compound that reduces the plant's ability to absorb nutrients when using coconut fiber as a substrate. Lime solution Ca(OH)₂ Alkaline, helps neutralize tannic acid, making coconut fiber safer for plants.
Method 3: Check the pH in the pot
Regularly check the pH of the growing medium and adjust if necessary with lime or buffer solution.
Method 4: Use additives to reduce tannins
Add organic buffers (such as treated manure) to neutralize the effects of tannins.

Not all tannins are harmful, and the degree of impact depends on the plant, the concentration of tannins in the soil, and the environment in which the plant lives. Some plants have evolved to adapt to or even use tannins to prevent competition from other species (allelopathy).