Leaf shapes in nature are very diverse. Let's learn about leaf morphology, describe and classify leaves in nature.
Morphological description of leaves
Leaves can be simple (a single leaf blade or leaflet) or compound (with several leaflets joined together). Here is an example of compound leaf terminology:

The leaves of indoor plants have extremely diverse shapes, partly because the leaves are the main part that bonsai players are interested in, from which people collect and even crossbreed to find new plants with special leaf shapes.
40 leaf shapes in nature
To help people understand more about leaves, Kla has translated 40 leaf shape terms most basic. Please see the image below.

Below are some examples of actual leaf shapes commonly found in some species. ornamental leaves, indoor plants.
Bipinnate leaves
Compound leaves are an evolved form of leaves in which each leaf blade is not directly attached to the stem but usually through a rachilla system.

The attachment point of the leaflet to the petiole does not have a dormant bud like the attachment point of the simple leaf to the stem, this is one of the characteristics that distinguishes the leaflet from the simple leaf.
Heart leaf (cordate)
Heart shaped leaves are perhaps the most common of all leaf shapes.

This shape is also familiar to people and has many positive meanings, especially symbolizing love, so trees with heart-shaped leaves are always grown by many people.
Spear-shaped leaves
Lanceolate leaves have many variations but have two easily recognizable characteristics: they always have a pointed tip and a petiole.

Leaf margins can be deformed or have many different shapes.
Lobed
Leaves with deeply indented margins are also called lobed leaves, but the leaf distribution is more even and the lobes are usually not close to the petiole, but the leaf blade is still quite large.
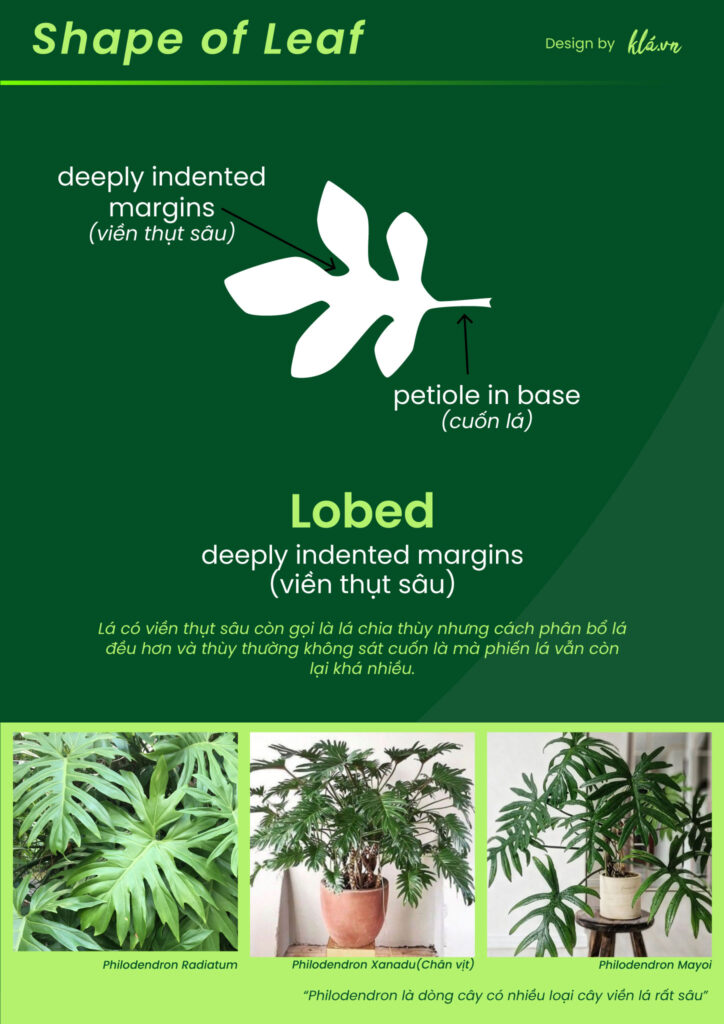
Many plants have this type of leaf margin, for example Monstera species and some varieties of philodendron.