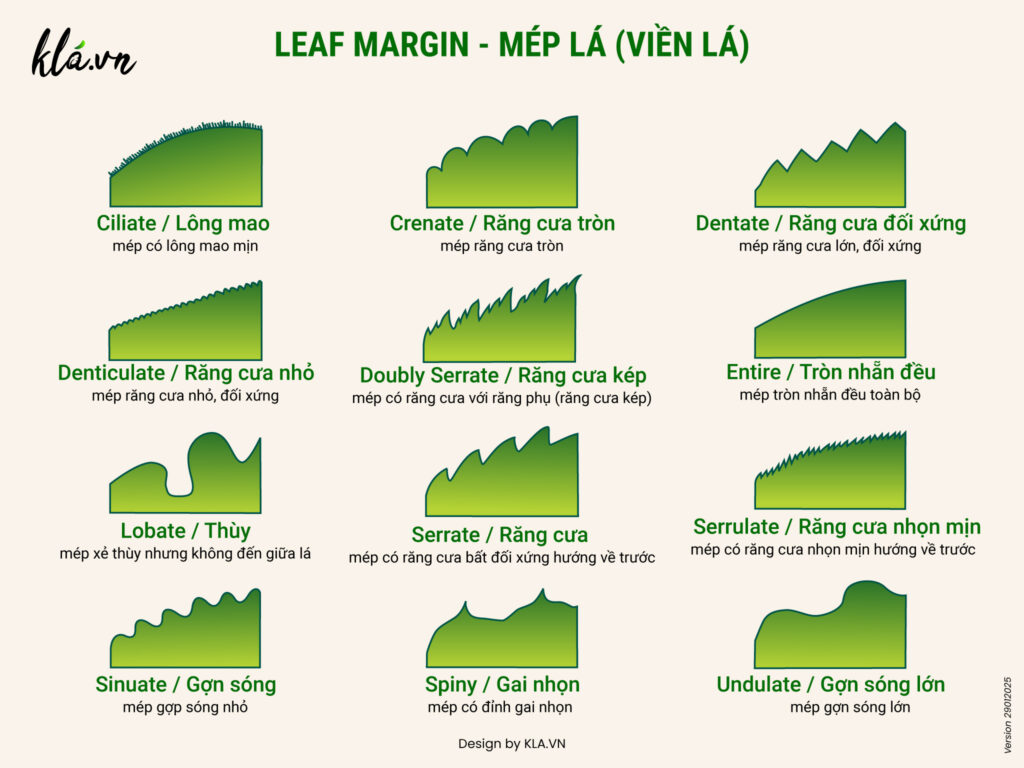
Leaf margins (leaf margins, leaf margins) are a common feature used to identify plants because they are often similar within a species or group of species. Leaf margins or leaf margins are both terms used to describe the outer circumference of a leaf.
Below are the 12 most common types of leaf margins (leaf margins) found in nature:
In addition, in nature there are many types of leaf edges (leaf edge) differently, leaf margins may vary depending on growing conditions, the growth stage of the leaf may also vary leaf shape speaking and the leaf edge in particular.
1. Ciliate margin
The ciliate margin is covered with fine hairs along the edge, giving it a smooth or fringed feel.

This feature helps reduce evaporation and prevents insects or pathogens from entering.
2. Crenate margin
The leaf margin has a rounded serration (crenate margin) consisting of rounded serrations, creating a soft, wavy border along the leaf edge.

This feature enhances drainage and can minimize damage from wind or insects.
3. Dentate margin
The leaf margin has a symmetrical dentate margin formed by outward-pointing serrations, arranged symmetrically along the leaf margin.

This feature increases the area for gas exchange and may contribute to protecting the plant from leaf-eating animals.
4. Rounded margin
The entire margin leaf has an entire margin, without teeth or lobes, forming a smooth and continuous border.

This feature helps reduce water loss and limit mechanical damage, suitable for dry or low-competition environments.
5. Double serrate margin
Doubly serrate margin leaves have margins with two levels of serration, where each large tooth is divided into smaller teeth.

This feature helps increase the gas exchange area and can improve drainage, limiting dew condensation on the leaves.
6. Denticulate margin
Denticulate margin leaves have margins formed by very small, even, and delicate serrations along the leaf margin.

This feature enhances drainage and can reduce attack by small insects.
7. Lobate margin
Lobate margin leaves have margins divided into shallow or deep lobes, forming characteristic curves along the leaf margin.

This feature increases the surface area for photosynthesis and can reduce wind resistance, protecting the plant in windy environments.
8. Serrate margin
Serrate margin leaves have edges with sharp teeth pointing towards the leaf tip, forming a sharp border.

This feature increases drainage and may serve as a defense against leaf-eating animals.
9. Serrulate margin
Serrulate margin leaves have margins with small, sharp, regular teeth, forming a smooth margin.

This feature helps the plant reduce insect infestation and protects the leaves from mechanical damage.
10. Sinuate margin
Sinuate margin leaves have wavy edges, forming gentle, irregular curves.

This feature increases wind resistance and can help reduce water loss in dry environmental conditions.
11. Spiny margin
Spiny margin leaves have edges with sharp spines growing along the leaf margin, forming a sharp fence.

This feature helps protect the plant from attack by leaf-eating animals and minimizes damage from chewing.
12. Large undulate margin
The undulate margin leaves have strongly wavy margins, forming large, distinct waves along the leaf margin.

This feature increases the surface area for photosynthesis and can reduce the impact of strong winds on the plant.